Fragments of Discontinuous Dna Synthesis Are Called
The replication of DNA is semiconservative and discontinuous. DNA polymerase III has a high processivity and therefore synthesizes DNA very quickly.
Dna Replication By Biology Experts Notes Medium
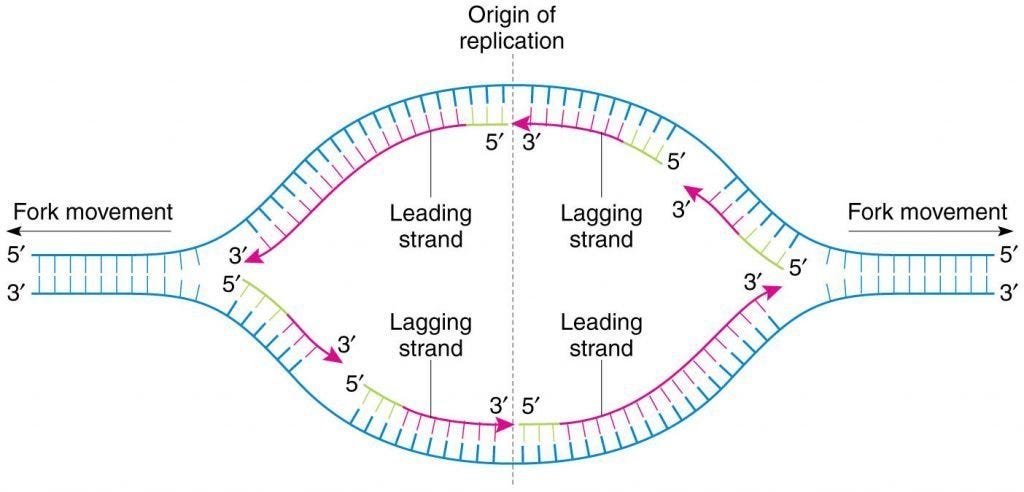
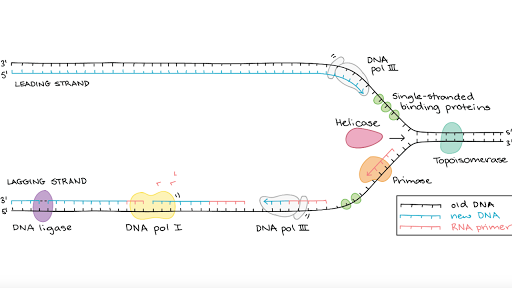
DNA replication proteins at the replication fork.

. And this happens when the two replication forks between the two terminals meet each other. So this DNA strand built up of Okazaki fragments is called a lagging strand. Okazaki fragments are then synthesized via extension of these RNA primers by DNA polymerase.
The lagging strand. The leading strand b. The lagging strand c.
The leading strand b. The helicase unwinds the duplex DNA and Single Strand Binding proteins SSBs coat and stabilize single. RNA that has hydrogen bonded to itself forms a.
On which strand is DNA synthesis discontinuous occurring in fragments that are later connected. This is an energy molecule that is part of the phosphate backbone and is used to link the DNA. Okazaki fragments that are not ligated could cause double-strand-breaks which cleaves the DNA.
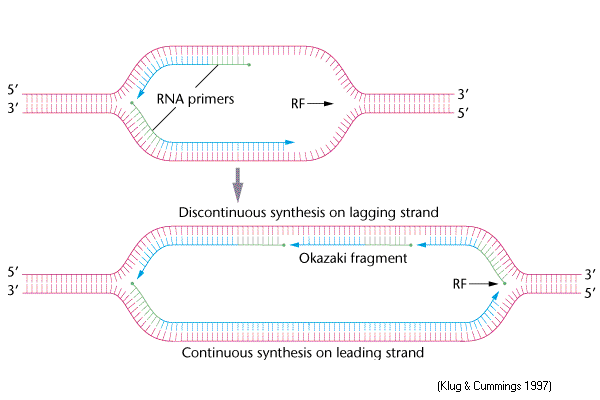
Synthesis of the other strand called the lagging strand is made possible through discontinuous synthesis of short fragments called Okazaki fragments in the 5 to 3 direction which are later joined together. RNA polymerase is guided by the. The newly formed segment is sealed by.
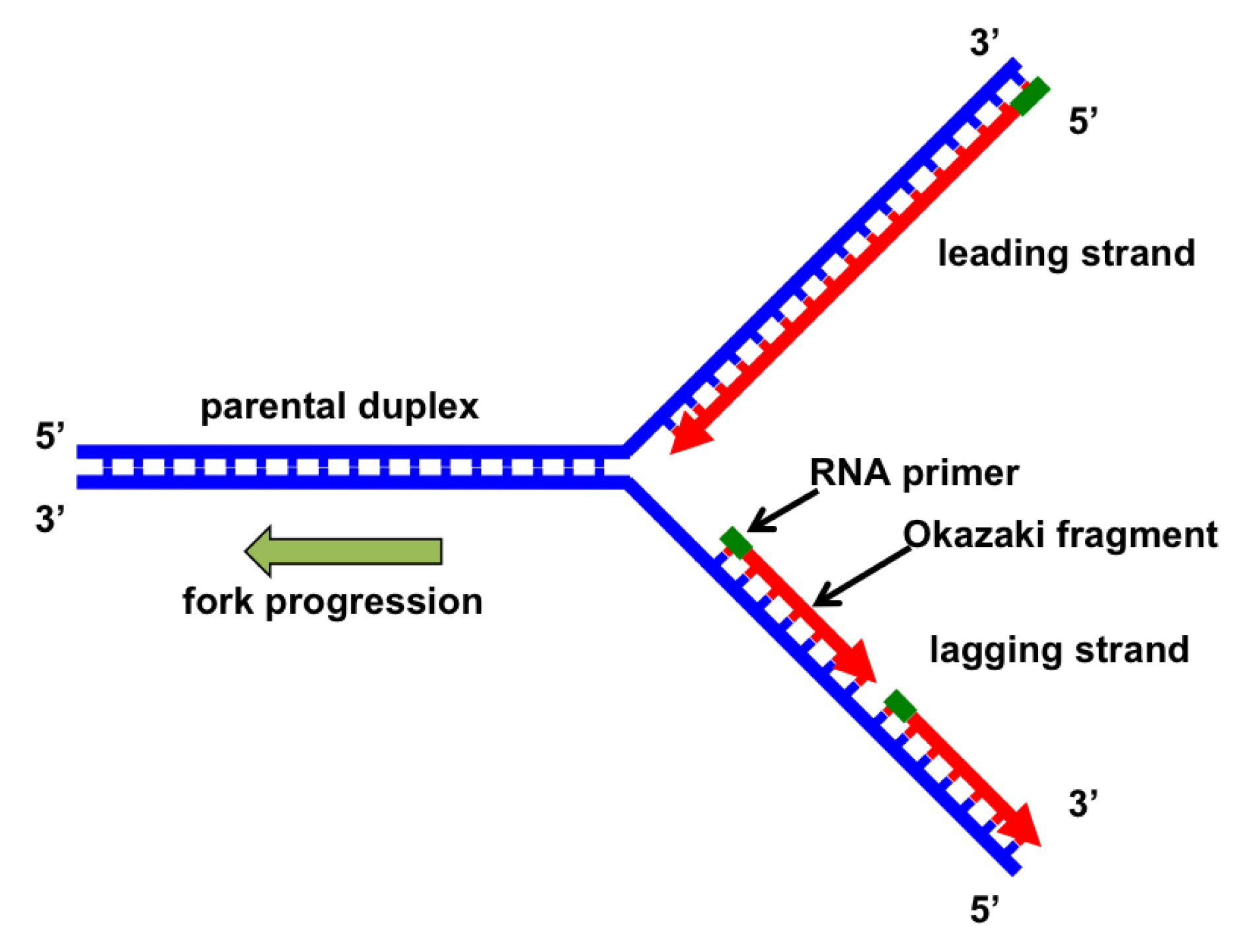
During DNA synthesis an ATP adenosine triphosphate molecule is created. In contrast to DNA synthesis the synthesis of RNA can initiate de novo and an enzyme called primase synthesizes short fragments of RNA eg three to ten nucleotides long complementary to the lagging strand template at the replication fork. Both strands synthesize DNA in fragments.
Termination of replication occurs in different ways in different organisms. In Ecoli like organisms chromosomes are circular. This strand is known as the lagging strand since the process of DNA synthesis on this strand proceeds at a lower rate.
DNA Synthesis and the Cell Cycle In animal cells including human cells the replication of the DNA genome occurs only during the synthetic or S phase. Why is the DNA synthesis of the lagging strand considered discontinuous. An enzyme called DNA ligase then joins the 3 end of the new DNA fragment to the 5 end of the previous one to complete the process Figures 5-13 and 5-14.
The reason for such a difference. The resulting small Okazaki fragments can contain 1000 to 2000 bases in bacteria but eukaryotes -- organisms having cells with nuclei -- have fragments of only 100 to 200 bases. This pulls apart the 2 phosphate backbone.
On the opposite strand DNA is synthesized in a discontinuous manner by generating a series small fragments of new DNA in the 5 3 direction. What is the initial target of RNA polymerase. The lagging strand c.
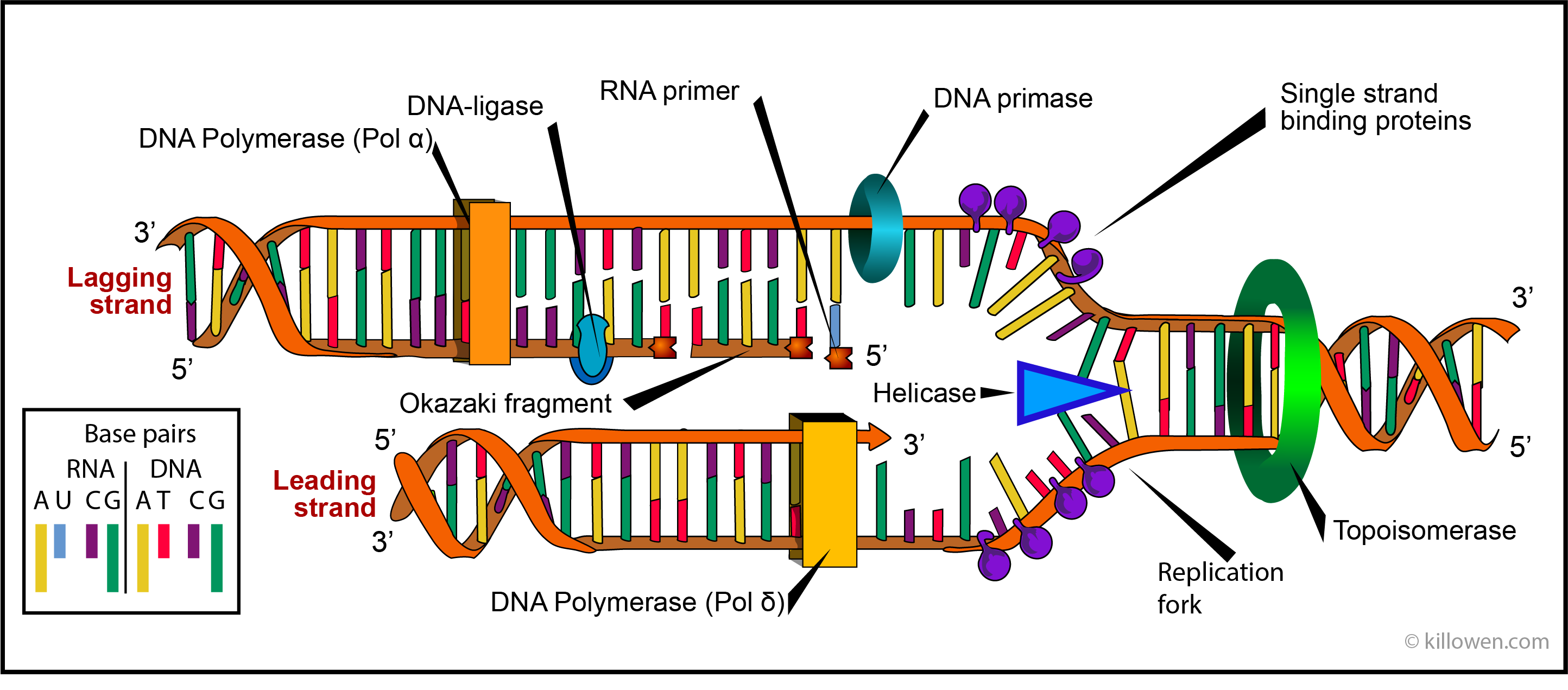
During lagging strand synthesis DNA ligase I connects the Okazaki fragments following replacement of the RNA primers with DNA nucleotides by DNA polymerase δ. They occur as fragments called Okazaki fragments. On which strand are new nucleotides being added in the same direction as the replication fork is opening.
The synthesis of the lagging strand by a discontinuous backstitching mechanism means that only the 5-to-3. This is a process where a cell makes an identical copy of its genome and then divides. The synthesis of one of the many DNA fragments on the lagging strand.
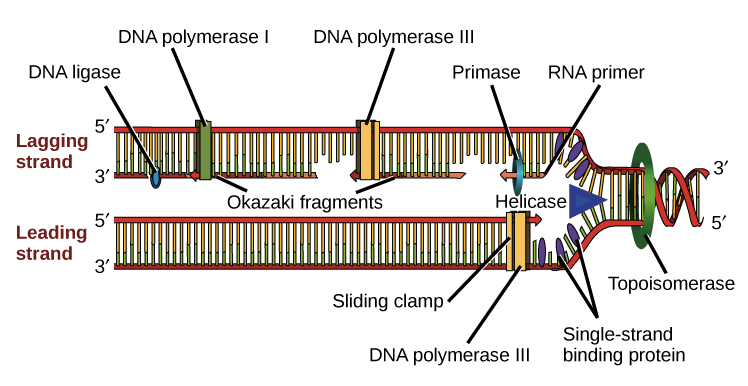
This is usually temporally separated from the mitotic phase by non synthetic periods referred to as gap 1 G1 and gap 2 G2 occurring before and after the S phase respectively The cell prepares for DNA. DNA ligase is the enzyme that binds adjacent Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand resulting in a continuous daughter strand where DNA polymerase had worked in a discontinuous fashion. An important consequence of such RNA.
However the synthesis is paused when it reaches 5 end of the RNA primer of the already-synthesized DNA stretch. Since only a small number of double-strand breaks are tolerated and only a small number can be repaired. This high processivity is due in part to the β-clamps that hold onto the DNA strands.
Taylor in 1957 labelled the root tip cells of broad bean with thymidine labelled with tritium 3 H. During DNA replication the synthesis of one strand occurs in a continuous manner whereas that of the other strand occurs in a discontinuous manner through the formation of fragments. The synthesis is moving in the opposite direction from the replication fork.
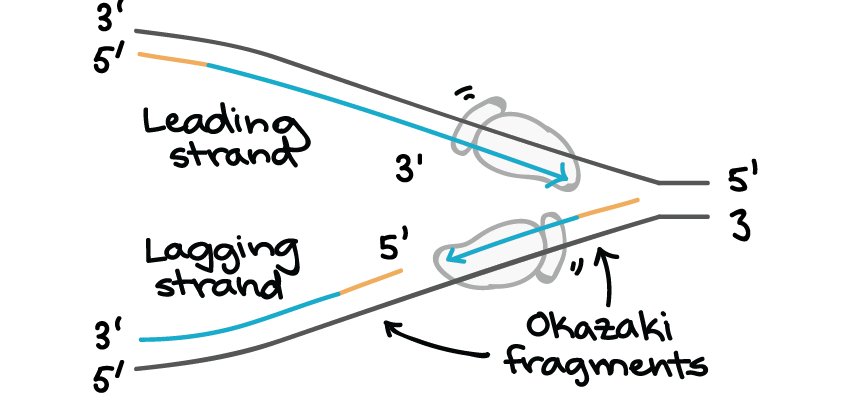
DNA polymerase goes back removes the wrong base allows the addition of the proper base and then proceeds forward. The former strand is termed as the leading strand the latter as the lagging strand and the intermediate fragments are termed as the Okazaki fragments. Lagging strand DNA ligase and discontinuous.
The enzyme called DNA ligase joins them later. The lagging strand unwinds in small sections that DNA polymerase replicates in the leading direction. DNA polymerase III will then synthesize a continuous or discontinuous strand of DNA depending if this is occurring on the leading or lagging strand Okazaki fragment of the DNA.
The events which lead to the initiation of DNA synthesis include synthesis of enzymes and other proteins required for DNA synthesis. The labelled cells were found to contain labelled chromatin during S period. The fragments terminate in an RNA primer that is.
Okazaki fragments are the short DNA fragments on the lagging strand formed during DNA. Proofreading and DNA repair. These fragments are called Okazaki fragments which are later joined to form a continuous chain of nucleotides.
Hence the DNA synthesis at the lagging strand is discontinuous and the resultant DNA stretches are known as Okazaki fragments. A wrong base is sometimes introduced during replication one in ten thousand. The double helix separates through a process known as unzipping.
Template strand of DNA.

Primer Molecular Biology Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia Dna Helicase Dna Replication Dna Polymerase

Tj The Enzymes A Portion Of The Double Helix Is Unwound By A Helicase A Molecule Of A Dna Polymerase Binds To One St Dna Ligase Dna Polymerase Study Biology

ป กพ นโดย Allison Lasky ใน Mcat เทคโนโลย การศ กษา ช วว ทยา

Semidiscontinuous Dna Replication Youtube
Continuous Discontinuous Synthesis
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Dna Replication Leading Strand Vs Lagging Strand Okazaki Fragments Youtube
Genes Free Full Text The Replication Fork Understanding The Eukaryotic Replication Machinery And The Challenges To Genome Duplication Html
7 Dna Synthesis Is Continuous And Discontinuous And Takes Place At Moving Replication Forks Labxchange

Okazaki Fragments Dna Replication The Bumbling Biochemist

Dna Replisome Replication Complex

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication

Dna Replication 2017 Vol 6 Mtg Biology Today Biology Study Chemistry Science Biology

Okazaki Fragments An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna Replication Of The Leading And Lagging Strand Learn Science At Scitable
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Dna Replication Concept Map Biology Notes Study Biology Teaching Biology
Comments
Post a Comment